“Environmental Drone Monitoring” is revolutionising our approach to conserving and understanding the natural world. This blog post explores how drones, at the forefront of technological innovation, are transforming environmental conservation efforts. From reforesting vast tracts of land to monitoring endangered species and assessing water quality, the use of drones is providing unprecedented insights and capabilities. As we delve into the multifaceted roles of drones, we’ll examine their applications, the significant benefits they offer, the ethical considerations they entail, and the ways in which they are shaping the future of environmental protection. Join us on a journey through the skies as we uncover the impact and potential of drones in the quest for a more sustainable planet.
Table of Contents
Accuracy and Resolution in Environmental Drone Monitoring
When discussing environmental drone monitoring, two critical factors that directly impact the effectiveness of this technology are accuracy and resolution. These aspects are essential for ensuring that the data collected by drones are reliable and detailed enough to inform and guide conservation efforts accurately.
Understanding Accuracy in Drone Monitoring
Accuracy in environmental drone monitoring refers to the precision of the measurements and data collected during drone flights. This precision is crucial when monitoring changes in environmental conditions, tracking wildlife populations, or assessing vegetation health. High accuracy ensures that the information gathered reflects real-world conditions as closely as possible, allowing conservationists to make informed decisions.
To enhance accuracy, drones are equipped with advanced navigation systems and sensors. GPS and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) technologies enable drones to fly predetermined paths with minimal deviation, ensuring that data collection is consistent and precise over time. This is particularly important when monitoring changes in an area across different seasons or years.
The Role of Resolution in Environmental Data
Resolution, on the other hand, pertains to the level of detail that the imagery or data collected by the drone can reveal. High-resolution images are capable of showing fine details of the environment, such as individual plants, small water bodies, or even specific animal species. This detail is invaluable for tasks like identifying diseased trees in a forest, spotting illegal logging activities, or observing the movements of small groups of animals.
In environmental drone monitoring, resolution is determined by the quality of the cameras and sensors onboard the drone. Technologies like multispectral and hyperspectral imaging go beyond what the naked eye can see, providing insights into plant health, water quality, and more through the detection of various wavelengths of light.
Integrating Accuracy and Resolution
For environmental scientists and conservationists, the integration of high accuracy and high resolution in drone technology means being able to monitor ecosystems and wildlife with unprecedented detail and reliability. This combination allows for the detection of subtle environmental changes, enabling early intervention and more effective conservation strategies.
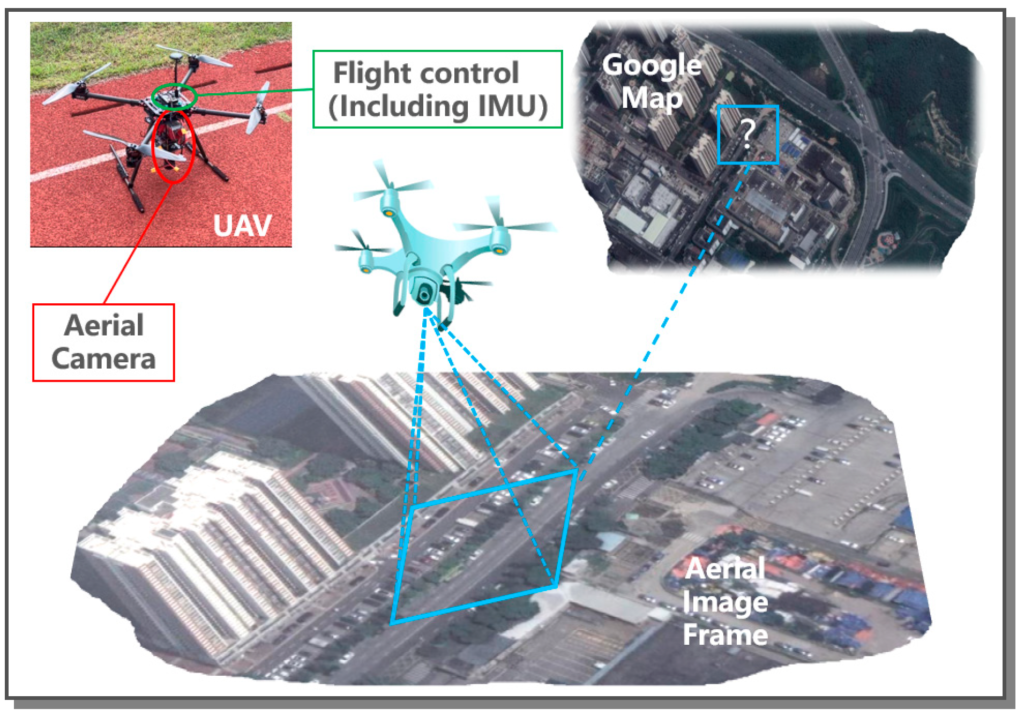
Incorporating these images will not only make the content more engaging but also help readers visualize the concepts of accuracy and resolution in environmental drone monitoring, enhancing their understanding of the topic.
Flight Time and Range in Environmental Drone Monitoring
In the realm of environmental drone monitoring, two crucial performance metrics significantly impact the scope and efficiency of data collection operations: flight time and range. These metrics determine how long a drone can stay airborne and the distance it can cover during a single mission, directly influencing the scale at which environmental assessments and conservation activities can be conducted.
The Importance of Flight Time
Flight time refers to the duration a drone can fly before needing a recharge or battery replacement. This is a pivotal factor in environmental monitoring, as longer flight times allow drones to cover more area or spend more time gathering detailed data over specific sites. Modern drones used in conservation and environmental monitoring can have flight times ranging from 20 minutes to several hours, depending on their design, battery technology, and operational conditions.
Extended flight times are particularly beneficial for comprehensive ecosystem assessments, tracking migratory patterns of wildlife, or conducting continuous surveillance of protected areas to prevent illegal activities such as poaching or deforestation. The longer a drone can stay in the air, the more data it can collect, making it an invaluable tool for environmental scientists and conservationists.
Understanding Range and Its Impact
The range of a drone defines how far it can travel from its control point while maintaining a reliable communication link. Like flight time, the range is critical for environmental drone monitoring, especially in large, remote, or inaccessible areas. Drones with extended ranges can venture further into these regions, providing data on ecosystems that might be difficult or impossible to gather through ground-based methods.
Advancements in drone technology and remote control systems have significantly increased the operational range of drones, with some models capable of traveling several kilometers from the operator. This extended reach is crucial for mapping large natural habitats, surveying environmental damage after natural disasters, or monitoring changes in land use over wide geographical areas.
Integrating Flight Time and Range for Enhanced Monitoring
The integration of long flight times and extensive ranges allows drones to conduct thorough and far-reaching environmental monitoring missions. This capability is essential for creating detailed, comprehensive maps of ecosystems, detecting environmental changes, and implementing timely conservation measures. The ability to cover vast distances without the need for frequent recharging or operator intervention makes drones an exceptionally efficient tool in the arsenal of environmental protection.
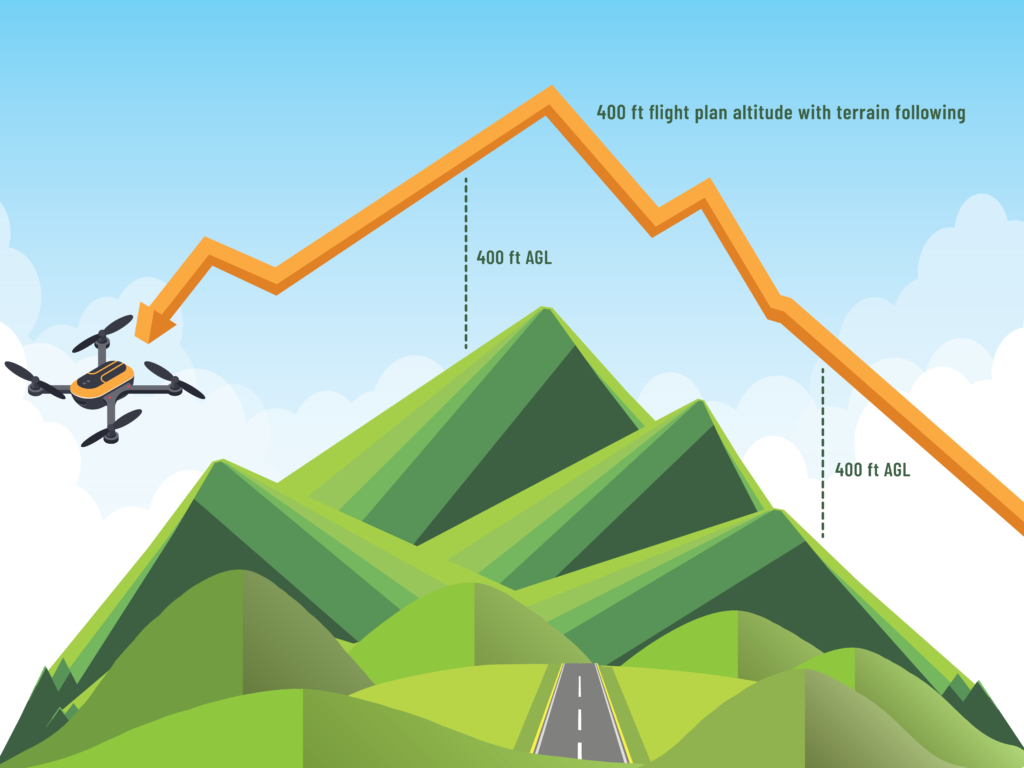
Incorporating these visuals will enrich the article, providing readers with clear, engaging examples of how flight time and range are pivotal in the successful application of drones for environmental monitoring purposes.
Data Processing and Analysis Software in Environmental Drone Monitoring
A pivotal aspect of environmental drone monitoring lies not just in the collection of data but in its subsequent processing and analysis. Data processing and analysis software transforms raw data collected by drones into actionable insights, enabling conservationists and environmental scientists to make informed decisions based on accurate, comprehensive environmental assessments. This software plays a crucial role in interpreting the vast amounts of data drones gather, from high-resolution imagery to multispectral scans, making it an indispensable tool in the field of eco-innovation.
Transforming Raw Data into Insightful Information
Once a drone completes its flight, the raw data it has collected needs to be processed. This is where data processing and analysis software comes into play. It converts raw imagery and sensor data into formats that are easier to interpret, such as maps, graphs, and 3D models. For instance, software can stitch together hundreds of aerial photographs to create detailed orthomosaic maps or use thermal imagery to assess wildlife populations.
The software also employs advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze environmental data. It can identify changes over time, such as deforestation rates, or detect specific features, like water bodies and their quality, with a high degree of accuracy. This capability is essential for monitoring ecosystem health, predicting environmental changes, and planning conservation efforts effectively.
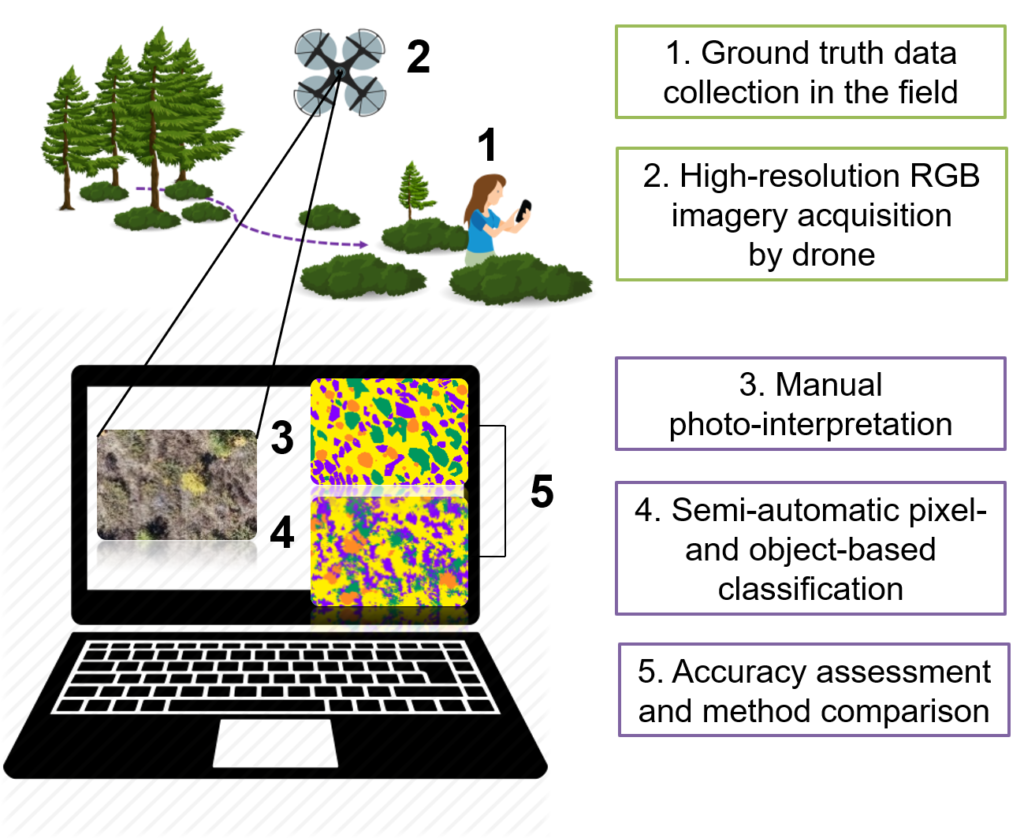
Enhancing Environmental Conservation Efforts
The insights derived from drone-collected data through processing and analysis software empower stakeholders to track environmental changes with unprecedented precision and speed. This enables prompt action in areas like habitat restoration, pollution control, and wildlife protection. Moreover, by facilitating the visualization of complex environmental data, the software helps communicate findings to a broader audience, raising awareness and support for conservation initiatives.
Incorporating these visuals will not only break up the text and add interest but also provide readers with a clearer understanding of the transformative power of data processing and analysis software in environmental drone monitoring.
Ease of Use in Environmental Drone Monitoring
The adoption and effectiveness of environmental drone monitoring technologies largely hinge on their ease of use. Drones and the accompanying software designed for environmental conservation must be accessible and manageable for operators with varying levels of expertise. This ensures that the benefits of drone technology can be fully leveraged by professionals and volunteers alike, contributing to the broader goals of environmental protection and conservation.
Simplifying Drone Operations
Modern environmental monitoring drones are engineered with user-friendly features that simplify operation. These include automated flight planning, where users can pre-program flight paths using GPS waypoints, and autonomous flight modes, allowing drones to take off, fly, and land with minimal human intervention. Additionally, safety features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functions enhance operational reliability and protect the drone from potential mishaps.
Ease of use is further exemplified in the drones’ design, with some models offering compact, foldable frames for easy transportation and quick setup in the field. This portability is crucial for environmental monitoring tasks in remote or difficult-to-access areas.
Streamlining Data Collection and Analysis
The software used for data processing and analysis is another critical aspect of the ease of use in environmental drone monitoring. Developers focus on creating intuitive user interfaces that guide users through the data processing steps, from importing raw data to visualizing the final analytical outputs. This software often includes tutorial resources, online support, and community forums to assist users in overcoming any challenges they encounter.
Moreover, the integration of cloud-based storage and processing capabilities allows users to access and analyze drone-collected data from anywhere, facilitating collaborative environmental monitoring projects and simplifying data management.
Training and Resources
To enhance ease of use, many drone manufacturers and software developers offer comprehensive training programs and resources. These can range from online tutorials and webinars to hands-on workshops, all aimed at equipping users with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively deploy drones in environmental conservation efforts.
Including these images will help illustrate the concept of ease of use in environmental drone monitoring, providing readers with a visual understanding of how these technologies are made accessible to a wide range of users.
Durability and Weather Resistance in Environmental Drone Monitoring
For drones to be effective in environmental monitoring and conservation, they must be capable of operating in various environmental conditions. Durability and weather resistance are crucial factors that determine a drone’s ability to perform under challenging conditions, such as in rain, wind, high humidity, or temperature extremes. These features ensure that drones can reliably collect data without risking damage to the equipment or loss of valuable information.
Understanding Durability in Drones
Durability refers to the drone’s ability to withstand physical stresses, including rough handling, impacts during landing, or collisions with objects like tree branches. Durable drones are typically constructed from high-strength materials such as carbon fiber or reinforced plastics, offering a balance between lightweight design and robustness. This construction helps protect sensitive components like cameras and sensors, ensuring the drone remains operational even after minor accidents.
The Importance of Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is equally important, as environmental monitoring often occurs in unpredictable and harsh weather conditions. Weather-resistant drones are designed with sealed bodies and components that protect against moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. This allows them to operate in a range of conditions, from tropical rainforests with high humidity to cold mountainous regions.
Some drones are specifically designed to function in adverse weather, equipped with features like heated batteries for cold environments or waterproof casings for flights in light rain. These adaptations expand the possibilities for environmental data collection, enabling studies and conservation efforts that were previously challenging due to weather limitations.
Enhancing Fieldwork Efficiency and Safety
Drones with high durability and weather resistance contribute significantly to the efficiency and safety of environmental monitoring projects. They minimise the risk of data loss due to equipment failure and reduce the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Moreover, by ensuring that drones can operate in a wide range of conditions, researchers and conservationists can plan fieldwork with greater flexibility and less concern for weather disruptions.

Incorporating these images will not only make the content more engaging but also help readers visualise the critical role that durability and weather resistance play in the success of environmental drone monitoring efforts.
Environmental Impact of Environmental Drone Monitoring
While drones are instrumental in advancing environmental monitoring and conservation efforts, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of the drones themselves. Sustainable practices in the production, operation, and disposal of drones ensure that their use in environmental conservation contributes positively to the ecosystem without causing harm. This aspect of environmental drone monitoring is crucial for maintaining the integrity and ethos of conservation work.
Minimising Carbon Footprint
Drones, especially those powered by electricity, have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to traditional manned aircraft used for similar monitoring purposes. Electric drones eliminate the emissions associated with the combustion of fossil fuels. However, the environmental impact of manufacturing batteries and the source of the electricity used for charging are important considerations. Manufacturers and operators can minimize this impact by opting for batteries with longer life spans, recycling used batteries, and utilizing renewable energy sources for charging.
Reducing Disturbance to Wildlife
One of the major advantages of using drones in environmental monitoring is their ability to collect data with minimal disturbance to wildlife and natural habitats. Unlike human presence, which can alter animal behavior and stress wildlife, drones can operate at a safe distance, making them an ethical choice for monitoring sensitive species and ecosystems. Selecting drones that produce less noise and are designed to blend with the environment further reduces their impact on wildlife.
Sustainable Production and Disposal
The environmental responsibility of drone use extends to their production and end-of-life disposal. Sustainable production practices, such as using recycled materials and minimising waste, contribute to the environmental ethos of drone monitoring. Additionally, proper disposal and recycling of drones and their components, including batteries, are essential to prevent pollution and reduce waste.

Incorporating these visuals can help underscore the key points about the environmental impact of drones used in monitoring, showcasing how they can be a part of sustainable conservation strategies. This approach not only informs but also reassures readers that environmental drone monitoring can align with ecological preservation and sustainability goals.
Regulatory Compliance in Environmental Drone Monitoring
Ensuring regulatory compliance is a crucial aspect of conducting environmental drone monitoring. As drones become increasingly integrated into conservation efforts, adhering to legal frameworks and aviation regulations becomes essential for both the success and legitimacy of these initiatives. This compliance encompasses a range of considerations, from airspace restrictions and privacy laws to environmental protection regulations.
Navigating Airspace Regulations
Airspace regulations vary significantly by country and region, often requiring drone operators to obtain permits or authorization before conducting flights, especially in protected or sensitive areas. These regulations are designed to ensure safety in the airspace, prevent conflicts with manned aircraft, and protect wildlife and ecosystems from potential disturbances caused by drones.
Operators must be aware of no-fly zones, altitude restrictions, and requirements for notifying or gaining approval from aviation authorities. Understanding these rules and obtaining the necessary permissions is the first step in ensuring that environmental drone monitoring projects are compliant and sustainable.
Respecting Privacy and Data Protection Laws
While drones are powerful tools for environmental monitoring, they also raise concerns regarding privacy and data protection. Regulations concerning the collection, storage, and sharing of data collected by drones must be strictly followed. This includes respecting the privacy of individuals who may inadvertently be captured in drone footage, especially in or near residential areas.
Operators should familiarize themselves with local privacy laws and ensure that their use of drones for environmental monitoring adheres to these legal requirements, including obtaining consent when necessary and protecting the data collected from unauthorized access.
Environmental Protection and Wildlife Laws
In addition to airspace and privacy regulations, environmental drone operators must consider laws aimed at protecting ecosystems and wildlife. This includes restrictions on flying in certain habitats to avoid disturbing animals, especially during sensitive periods such as breeding seasons.
Compliance with environmental protection laws not only ensures the legality of drone operations but also aligns with the ethical considerations of conservation work, emphasizing the importance of minimizing the ecological footprint of drone activities.

Including these visuals will not only make the content more engaging but also help readers visualize the practical aspects of ensuring regulatory compliance in environmental drone monitoring. This adds a crucial layer of understanding to the responsibilities of drone operators in the field of conservation.
Cost and Value for Money in Environmental Drone Monitoring
Evaluating the cost and value for money of drones used in environmental monitoring is essential for conservation organizations, researchers, and businesses aiming to invest in this technology. With a wide range of drone options available, understanding the balance between cost, features, and long-term benefits is key to making informed decisions that align with budget constraints and project objectives.
Initial Investment vs. Operational Costs
The initial investment in drone technology includes the purchase price of the drone itself, along with any additional equipment such as cameras, sensors, and batteries. High-end drones equipped with advanced imaging technology and longer flight times can be significantly more expensive, but they also offer more detailed data and greater efficiency in data collection.
Operational costs, on the other hand, cover maintenance, repairs, software subscriptions for data processing and analysis, and potential regulatory compliance fees. While some drones may have a higher upfront cost, their durability and lower maintenance requirements can offer better value for money in the long run.
Assessing Long-term Benefits
The value of investing in drone technology for environmental monitoring extends beyond immediate cost considerations. Drones can dramatically reduce the time and resources needed for data collection, accessing remote or difficult terrain with ease and providing insights that might not be possible through traditional methods. This efficiency can lead to significant cost savings over time, especially for large-scale or ongoing conservation projects.
Additionally, the quality and breadth of data collected by drones can enhance environmental research and conservation efforts, leading to better-informed decisions and more effective interventions. This intangible value, while difficult to quantify, is a critical consideration in assessing the overall worth of drone technology in environmental monitoring.
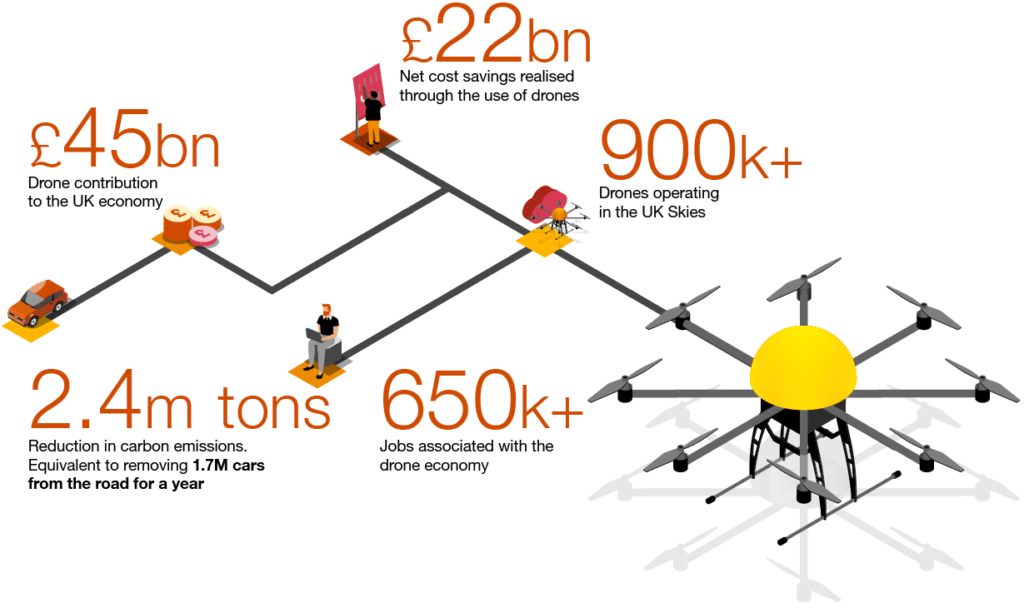
Including these visuals will not only enhance the appeal of the content but also help readers understand the economic considerations of drone technology in environmental monitoring. By highlighting both the costs and the value it brings to conservation efforts, the article can offer a balanced perspective on the investment in drones for environmental purposes.
Scalability and Integration in Environmental Drone Monitoring
Scalability and integration are key considerations for environmental drone monitoring programs looking to maximize their impact and efficiency. As conservation efforts and environmental research evolve, the ability to expand and adapt drone operations becomes crucial. Similarly, integrating drone-collected data with other environmental monitoring systems and data platforms enhances the value and applicability of the information gathered.
Expanding Drone Operations
Scalability refers to the ability to increase the size or scope of drone monitoring activities efficiently. This might involve deploying more drones to cover larger areas, upgrading existing drones with more advanced sensors for detailed data collection, or employing more sophisticated data analysis software as project needs grow. A scalable drone program can adapt to changing environmental monitoring requirements, from local habitat assessments to wide-scale environmental impact studies.
Key factors that contribute to the scalability of drone monitoring include the modular design of drones, which allows for easy upgrades and customization, and the availability of drones and sensors to suit a wide range of budgets and technical requirements. Planning for scalability from the outset ensures that drone operations can grow in tandem with project ambitions and conservation goals.
Integrating with Other Systems
Integration involves connecting drone-collected data with other environmental monitoring systems, databases, and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) platforms. This connection allows for the comprehensive analysis of environmental data, combining aerial insights from drones with ground-based observations, satellite imagery, and historical data sets.
Effective integration facilitates a holistic view of environmental conditions, supporting more accurate and informed decision-making. It also enables the automation of data workflows, where data collected by drones is automatically uploaded, processed, and analyzed alongside other environmental data, streamlining the monitoring process and reducing manual data handling.
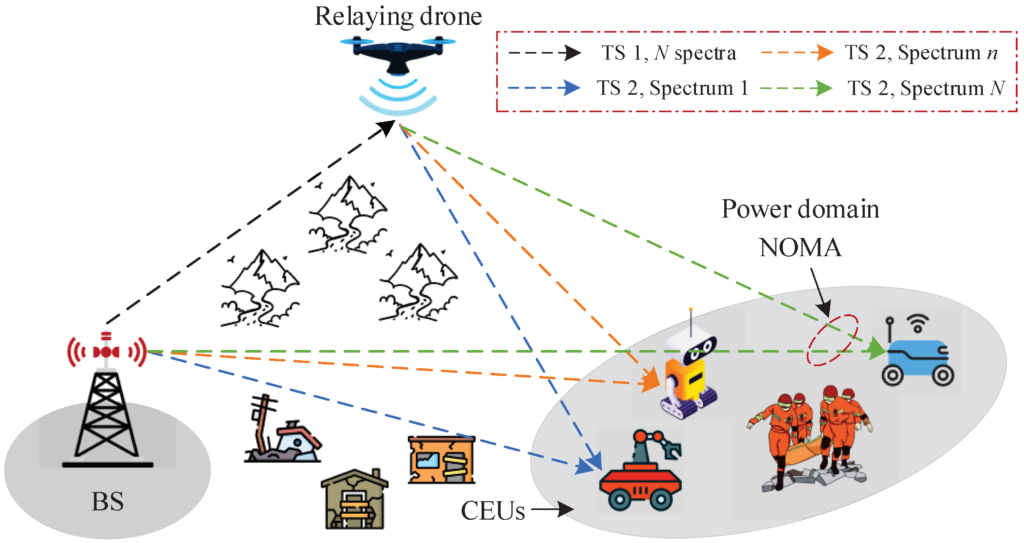
Including these visuals will not only make the content more engaging but also help readers visualize the practical aspects of scalability and integration in environmental drone monitoring. By showcasing examples of how drone operations can grow and interact with other data systems, the article can effectively convey the importance of these considerations in achieving comprehensive and effective environmental monitoring.
Community and Support in Environmental Drone Monitoring
The success of environmental drone monitoring efforts is not solely dependent on the technology itself but also on the community and support structures that surround it. Engaging with a community of drone enthusiasts, conservationists, and environmental scientists can provide invaluable insights, resources, and assistance. Similarly, having access to robust support from drone manufacturers and software developers is crucial for troubleshooting, updates, and learning best practices in drone operation and data analysis.
The Role of Community Engagement
Community engagement in the context of environmental drone monitoring involves connecting with individuals and organizations who share similar goals and interests. Online forums, social media groups, and conferences are excellent venues for exchanging ideas, experiences, and technical advice. These platforms allow drone operators to learn from others’ successes and challenges, discover new applications for drone technology in conservation, and collaborate on projects that can benefit from shared knowledge and resources.
Engaging with the community also opens up opportunities for advocacy and education about the importance of environmental conservation and the role of drones in supporting these efforts. By sharing stories and data from drone monitoring projects, individuals and organizations can raise awareness and encourage more people to contribute to environmental protection initiatives.
Importance of Manufacturer and Software Support
Support from drone manufacturers and software developers is another critical component of a successful environmental drone monitoring program. This support can take many forms, including customer service for technical issues, forums for user questions, and regular updates that improve drone performance and data analysis capabilities.
Additionally, training materials such as manuals, video tutorials, and webinars can help new users quickly become proficient in drone operation and data processing. For more advanced users, access to detailed technical documentation and the ability to request new features or report bugs is essential for pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with drone technology in environmental monitoring.

Incorporating these images will not only make the article more visually appealing but also underscore the importance of community and support in enhancing the effectiveness and impact of environmental drone monitoring efforts. Through engaging visuals, readers can better appreciate the collaborative and supportive aspects of using drones in conservation and environmental science.
Innovations and Unique Features in Environmental Drone Monitoring
The field of environmental drone monitoring is rapidly evolving, with new innovations and unique features continually emerging. These advancements are designed to enhance the capabilities of drones, making them more effective and versatile tools for conservation and environmental research. From advanced imaging technologies to autonomous flight capabilities, the latest innovations are pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in monitoring ecosystems, wildlife, and environmental changes.
Advanced Imaging Technologies
One of the most significant areas of innovation in environmental drone monitoring is in imaging technology. Drones equipped with multispectral, hyperspectral, and thermal cameras can capture a wide range of data that is not visible to the naked eye. This includes information on plant health, water temperature, and the presence of specific minerals in the soil. Such detailed environmental data is invaluable for research and conservation efforts, allowing for the early detection of issues such as disease in crops or vegetation, water contamination, and illegal mining activities.
Autonomous Flight and Data Collection
Autonomous flight capabilities are another innovative feature that enhances the efficiency of drone operations. Drones with advanced navigation systems can fly predetermined routes with minimal human intervention, ensuring consistent data collection over time and across large areas. This automation extends to data processing, where AI and machine learning algorithms analyze the collected data, identifying patterns and changes that may require further investigation or immediate action.
Enhanced Durability and Sustainability
Innovations in drone design and materials are also contributing to the durability and sustainability of environmental monitoring drones. New materials that are lighter and more resilient, combined with designs that are more aerodynamic, allow drones to operate in a wider range of conditions while reducing the environmental impact associated with their production and disposal. Some drones are now being designed with biodegradable components, further minimizing their environmental footprint.
Unique Features for Specific Environmental Tasks
Drones are also being customized with unique features tailored to specific environmental monitoring tasks. For example, drones used in reforestation projects may be equipped with seed dispersal mechanisms, allowing them to plant thousands of seeds over large areas much more quickly and efficiently than manual planting methods. Similarly, drones used in marine research can be fitted with waterproofing and salt resistance for safe operation over oceans and coastal areas.
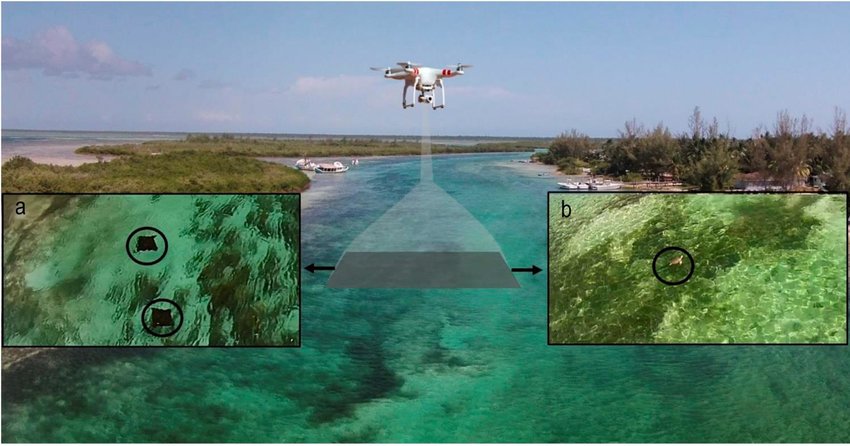
Incorporating these images will not only make the content more engaging but also visually demonstrate the cutting-edge innovations and unique features that are making drones an increasingly indispensable tool in environmental monitoring and conservation.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications in Environmental Drone Monitoring
Exploring case studies and real-world applications sheds light on the practical benefits and transformative impact of drones in environmental drone monitoring. These examples illustrate how innovative drone technology is being applied across diverse ecosystems and challenges, from conserving endangered species to combating climate change. Highlighting specific projects and their outcomes provides insight into the versatility and effectiveness of drones in environmental conservation efforts.
Reforestation Efforts in Mangrove Forests
One notable case study involves the use of drones for reforesting degraded mangrove forests. In Myanmar, drones were deployed to disperse thousands of seed pods over vast areas of cleared mangrove forests. Equipped with specialized seed dispersal mechanisms, these drones planted seeds more efficiently and at a fraction of the cost and time required for traditional reforestation methods. The project not only demonstrated drones’ potential to accelerate reforestation efforts but also highlighted their role in restoring ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity.
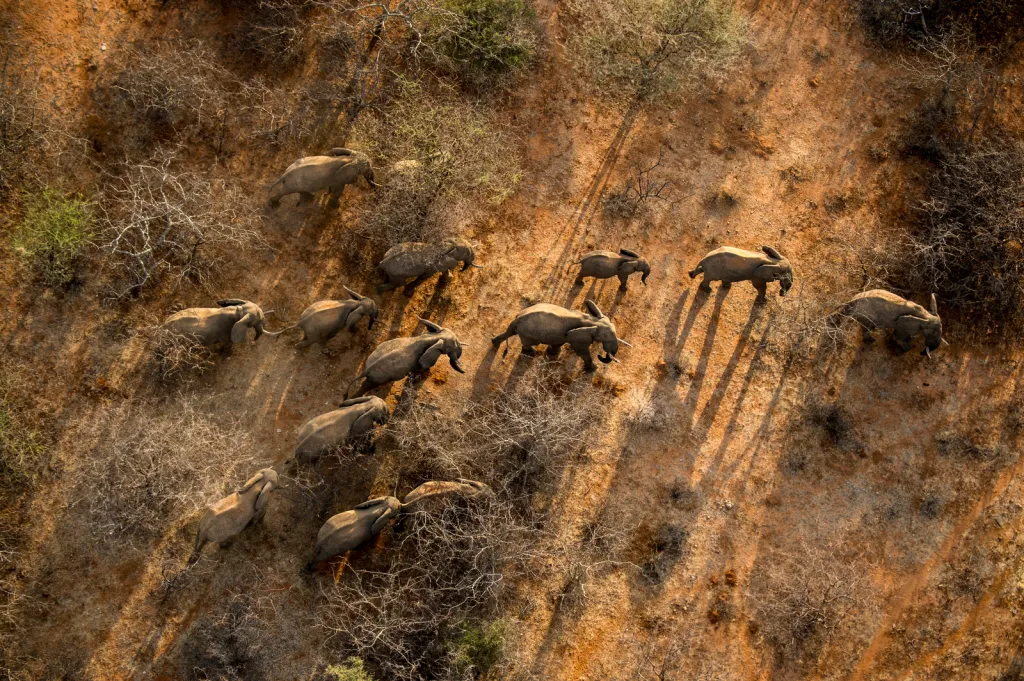
Wildlife Monitoring in Africa
Another significant application of drones is in wildlife monitoring and anti-poaching efforts in Africa. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras have been used to track endangered species, such as elephants and rhinos, providing conservationists with valuable data on their movements and behavior. Additionally, these drones have been effective in deterring poachers, significantly reducing poaching incidents in protected areas. This use of drones showcases their vital role in protecting wildlife and supporting conservation initiatives.
Water Quality Assessment in the United States
In the United States, environmental researchers have utilized drones to monitor water quality in lakes and rivers. By equipping drones with water sampling devices and sensors, scientists have been able to gather data on water temperature, pH levels, and contaminant presence in hard-to-reach areas. This approach has improved the efficiency and accuracy of water quality assessments, aiding in the detection of pollution sources and the implementation of appropriate mitigation strategies.

These case studies and real-world applications underscore the diverse and impactful ways in which drones are being utilized in environmental monitoring and conservation. By providing visual examples of drones in action, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the practical applications and benefits of this technology in addressing environmental challenges.
Future Proofing and Updates in Environmental Drone Monitoring
In the rapidly evolving field of environmental drone monitoring, staying current with technological advancements and ensuring systems are future-proofed is essential. Future proofing involves adopting flexible, upgradable drone technologies and software that can adapt to future environmental monitoring needs and technological advancements. Regular updates and maintenance are crucial components of this strategy, ensuring drones remain effective, efficient, and relevant over time.
Embracing Modular Design and Upgradability
Modular design in drones allows for easy component upgrades, such as sensors, cameras, or batteries, without the need to replace the entire drone. This approach not only extends the lifespan of the drone but also ensures that environmental monitoring efforts can benefit from the latest technological advancements. By selecting drones with modular capabilities, organizations can future-proof their investment, adapting to new monitoring requirements as they arise.
Importance of Software Updates and Maintenance
Software plays a critical role in the functionality and efficiency of drones for environmental monitoring. Regular software updates and maintenance are vital for enhancing features, improving data processing algorithms, and fixing any vulnerabilities. These updates can also add new functionalities to drones, such as improved data analysis tools or more efficient flight planning algorithms, ensuring the software continues to meet the evolving needs of environmental conservation efforts.
Staying Ahead with Continuous Learning and Training
As drone technology and environmental monitoring techniques continue to advance, ongoing learning and training become essential for operators. Engaging in continuous education and training programs allows drone operators and environmental scientists to stay abreast of the latest trends, regulatory changes, and best practices in drone usage. This proactive approach ensures that environmental monitoring efforts remain effective and that organizations can fully leverage the capabilities of their drone technology.

Including these visuals will not only enhance the article’s appeal but also provide concrete examples of how future-proofing and regular updates contribute to the longevity and effectiveness of drones in environmental monitoring. By illustrating these concepts, readers can better understand the importance of adaptability and ongoing education in leveraging drone technology for environmental conservation.
Ethical Considerations in Environmental Drone Monitoring
As the use of drones in environmental monitoring continues to grow, so too does the importance of addressing the ethical considerations associated with their deployment. Ethical drone use ensures that monitoring efforts are conducted responsibly, respecting privacy, wildlife, and the natural environment. It involves careful planning and adherence to ethical guidelines to mitigate any potential negative impacts on ecosystems and communities.
Respecting Privacy and Community Rights
When drones are used in close proximity to residential areas or community lands, privacy concerns become paramount. It’s essential to obtain consent from local communities and individuals before conducting drone flights. Transparent communication about the purpose, scope, and duration of the monitoring activities helps build trust and cooperation. Implementing strict data handling and access policies further ensures that any imagery or data collected that could infringe on privacy rights is managed responsibly.
Minimizing Disturbance to Wildlife
Drones can sometimes cause stress or disturbance to wildlife, particularly if flown too close or in sensitive habitats. Adhering to wildlife protection guidelines, such as maintaining a safe distance and avoiding critical breeding or nesting areas, minimizes potential disturbances. Using drones with noise-reduction technologies and conducting flights during times when animals are less active are practices that can further reduce impact on wildlife.
Environmental Impact of Drone Use
The production, operation, and disposal of drones all have environmental footprints that must be considered. Choosing drones made from sustainable materials, optimizing flight plans to minimize energy consumption, and properly recycling drones and their batteries at the end of their life cycle are steps that can help mitigate these impacts. It’s also crucial to evaluate the necessity of drone flights to ensure that the environmental benefits of the monitoring outweigh the ecological footprint of the drone operations themselves.
Incorporating these ethical considerations into environmental drone monitoring projects not only ensures that the technology is used in a manner that is respectful to people and nature but also contributes to the sustainability and social acceptance of drone use in conservation efforts. Through thoughtful planning and adherence to ethical guidelines, drones can continue to play a vital role in environmental protection while minimizing their potential for harm.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Environmental Monitoring with Drones
The integration of drones into environmental monitoring and conservation represents a significant leap forward in our collective efforts to understand and protect our natural world. As we have explored through various topics, from the innovative applications and unique features of drones to the ethical considerations and future-proofing strategies, it’s clear that drones offer unparalleled opportunities for enhancing environmental research, conservation, and advocacy.
Drones are transforming the landscape of environmental monitoring, providing data and insights with an efficiency and scale previously unimaginable. Their ability to reach remote areas, collect high-resolution data, and operate with minimal environmental impact underscores their potential as a cornerstone of modern conservation strategies. However, the journey doesn’t stop with technology alone. The successful integration of drones into environmental efforts hinges on our collective responsibility to ensure they are used ethically, sustainably, and in a manner that respects both nature and community rights.
As we look to the future, the ongoing advancements in drone technology, coupled with a deepening understanding of ecological systems, promise to open new horizons in environmental protection. By embracing these technologies, staying informed about best practices, and fostering a community of collaboration and support, we can ensure that drones continue to play a pivotal role in safeguarding our planet.
Yet, the true value of drones extends beyond the technology itself—it lies in the commitment of individuals and organizations worldwide to leverage this technology for the greater good. By continually assessing and addressing the ethical implications of drone use, ensuring regulatory compliance, and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible through innovation and collaboration, we stand on the cusp of a new era in environmental conservation.
In conclusion, drones in environmental monitoring embody the spirit of eco-innovation, offering a powerful tool in our quest to preserve and protect the Earth’s precious ecosystems. As we move forward, it is incumbent upon us all to harness this potential responsibly, ensuring that our skies—and the environments they survey—remain vibrant and thriving for generations to come.
Let us continue to explore, innovate, and advocate for the planet with drones as our allies in the enduring mission of environmental conservation.





Pingback: Why Chinese Drones are Dominating the Market in 2024: A Detailed Review - Drone Gigs